Cardiac Arrest - Adult
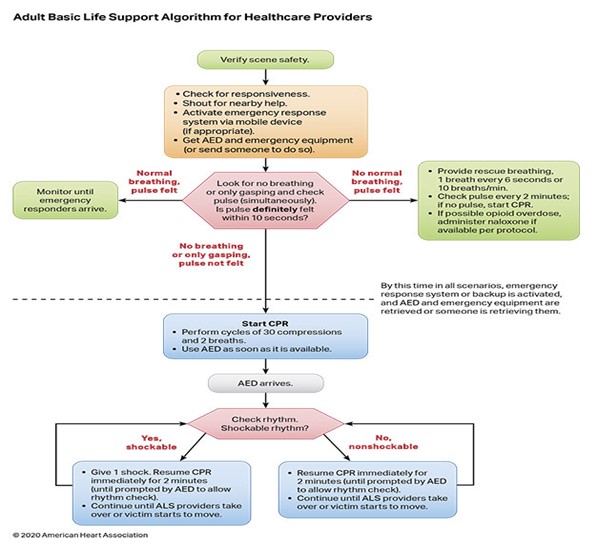
EMT STANDING ORDERS
- Routine Patient Care.
- Follow BLS guidelines as trained and credentialed.
- Check responsiveness.
- Call for advance team.
- Check the patient's breathing and pulse (for at least 5 but no more than 10 seconds), check breathing and pulse simultaneously.
- If no pulse, perform high-quality chest compression (CPR) and rescue breath (30 compressions: 2 rescue breaths).
- Apply AED and analyze the rhythm ASAP. Follow AED protocol.
- Continue CPR and AED cycles until the advance unit arrives or pulse is present.
- Call for AEMT/Paramedic intercept. & Assisst AEMT/Paramedic in patient care.
Note: Push hard and Push fast, Minimize Interruption for less than 10 seconds.
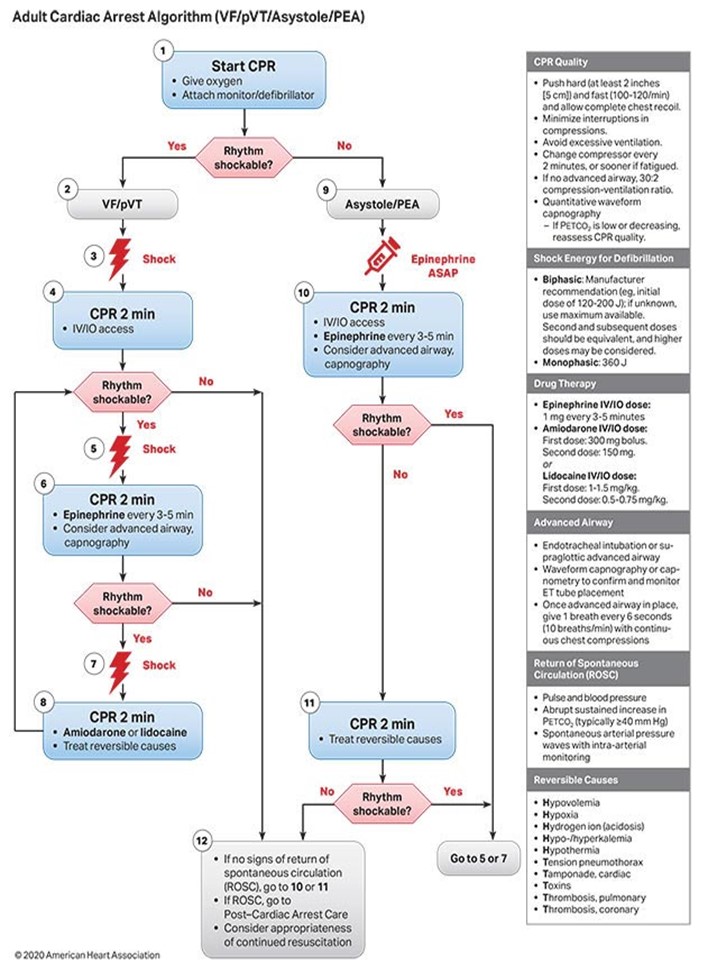
VF/Pulseless VT
AEMT/PARAMEDIC STANDING ORDERS
- Follow ACLS guidelines as trained and credentialed.
- Defibrillation when available, with minimum interruption in chest compressions. Resume CPR for 2 minutes; then rhythm check, if there is no pulse; start defibrillation. Use the manufacturer’s recommendations. (Corpulse monitor 200 joules).
- If no response after the second defibrillation and along with CPR:
- Administer epinephrine (1:10,000) 1 mg IV/IO; repeat every 3-5 minutes.
- Amiodarone 300 mg IV/IO, repeat dose 150 mg as needed OR Lidocaine 1 - 1.5 mg/kg IV/IO, repeat dose 0.5 - 0.75 mg/kg (Maximum total dose 3 mg/kg).
- Consider advanced airway only if airway patency cannot be maintained using basic maneuvers and adjuncts.
- Consider and treat reversible causes.
PEA / Asystole
AEMT/PARAMEDIC STANDING ORDERS
- Confirm PEA/Asystole.
- Establish IV/ IO access.
- Administer Epinephrine (1:10,000) 1 mg IV/IO; repeat every 3-5 minutes ASAP.
- Continue CPR (30 compressions: 2 rescue breaths).
- Consider advanced airway, and capnography, and confirm tube placement as per protocol.
- Consider and treat reversible causes.
- In PEA: Check a pulse every 2 minutes.
| Cause | Management |
|---|---|
| Hypovolemia | Volume infusion |
| Hypoxia | Ventilation and Oxygenation as needed |
| Hydrogen Ions ( acidosis) | Ventilation / Sodium bicarbonate |
| Hypo/hyperkalemia | Sodium bicarbonate/ Calcium Chloride |
| Hypothermia | Rewarming |
| Tension pneumothorax | Needle decompression |
| Tamponade, cardiac | Pericardiocentesis |
| Toxins | Antidote |
| Thrombosis, pulmonary | Fibrinolytic therapy |