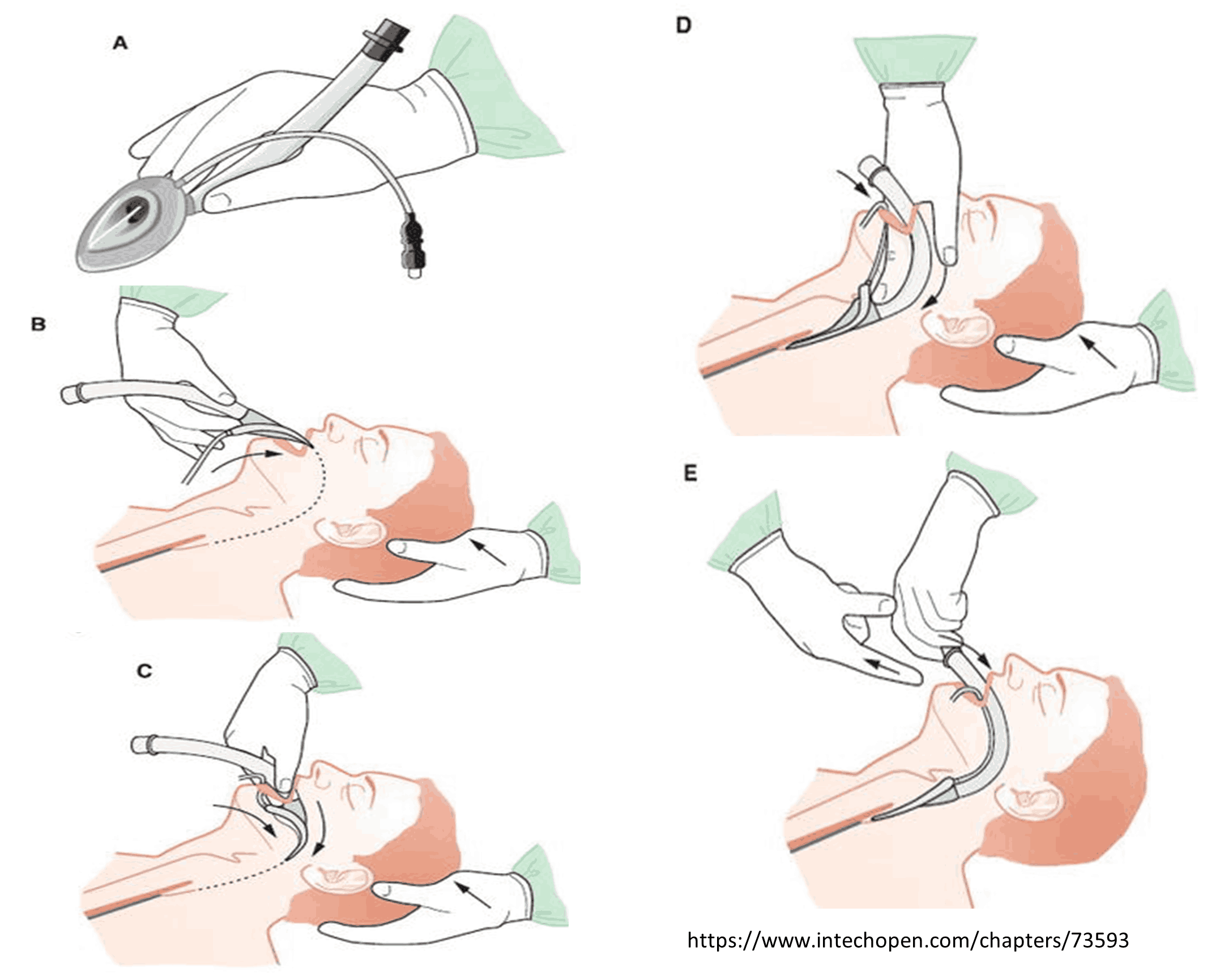
Supraglottic Airway (Adult & Pediatric)
This protocol applies to commercially available supraglottic airway devices. These airways must be used as directed by the manufacturer’s guidelines. They may be used in all age groups for which the devices are designed. Providers must be trained on and competent with the airway device they will be using.
Note: Double Lumen Devices (e.g., Combitube) are no
INDICATIONS:
- Cardiac Arrest.
- Inability to adequately ventilate a patient with a bag-valve-mask or longer EMS transports requiring a more definitive airway.
- Back up device for failed endotracheal intubation attempt.
RELATIVE CONTRAINDICATIONS:
- Severe maxillofacial or oral trauma.
- For devices inserted into the esophagus:
- The patient has known esophageal disease.
- The patient has ingested a caustic substance.
- The patient has burns involving the airway
PROCEDURE:
- Insertion procedure should follow manufacturer guidelines as each device is unique.
- Confirm appropriate placement by symmetrical chest-wall rise, auscultation of equal breath sounds over the chest and a lack of epigastric sounds with bag valve mask ventilation, and waveform capnography, if available.
- Secure the device.
- Document the time, provider, provider level and success of the procedure. Complete all applicable airway confirmation fields including chest rise, bilateral, equal breath sounds, absence of epigastric sounds and end-tidal CO2 readings.
- Reassess placement frequently, especially after patient movement.
POST TUBE PLACEMENT CARE - ADULT AND PEDIATRIC
Sedation:
- Fentanyl 50 - 100 mcg (pediatric dose 1 mcg/kg) slow IV/IO push. May repeat every 15 minutes as needed for anesthesia (maximum 300 mcg).
- Midazolam 2.5 - 5 mg IV/IO (pediatric dose 0.1 mg/kg IV/IO) every 5 – 10 minutes as needed for sedation (maximum 20 mg).
Contact Medical Director for additional dosing.